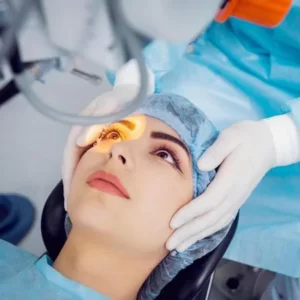
CATARACT TREATMENT
Cataract surgery involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. The artificial lens, called an intraocular lens, is positioned in the same place as your natural lens. It remains a permanent part of your eye. For some people, other eye problems prohibit the use of an artificial lens.
REFRACTIVE ERROR
Refractive error means that the shape of your eye does not bend light correctly, resulting in a blurred image. The main types of refractive errors are myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), presbyopia (loss of near vision with age), and astigmatism.

COMPUTER VISION SYNDROME
Computer vision syndrome, also referred to as digital eye strain, describes a group of eye- and vision-related problems that result from prolonged computer, tablet, e-reader and cell phone use.
GLAUCOMA TREATMENT
The damage caused by glaucoma can’t be reversed. But treatment and regular checkups can help slow or prevent vision loss, especially if you catch the disease in its early stages.
Glaucoma is treated by lowering your eye pressure (intraocular pressure). Depending on your situation, your options may include prescription eyedrops, oral medications, laser treatment, surgery or a combination of any of these.

DIABETIC RETINOPATHY TREATMENT
Diabetic retinopathy is best diagnosed with a comprehensive dilated eye exam. For this exam, drops placed in your eyes widen (dilate) your pupils to allow your doctor a better view inside your eyes. The drops can cause your close vision to blur until they wear off, several hours later.
UVEA AND RETINA TREATMENT
The uveal tract is the middle layer of the eye, divided into the anterior uvea (iris, ciliary body) and posterior uvea (choroid). The uvea is sandwiched between an outer layer (sclera) and an inner layer (retina). The anterior segment is separated from the posterior segment by the lens.